SPINNER Rigid Coaxial Lines components - robust performance
A rigid coaxial transmission line is mainly used in broadcast systems to transmit radio frequency signals between transmitter and combiners as well as between combiners and the antenna. The advantage of rigid coaxial lines is that the radiation leakage and attenuation, especially at higher frequencies, is lower than with flexible coaxial cables. This means that greater power can be transmitted, and higher shielding attenuation can be achieved.
Outstanding RF characteristics, best possible passive intermodulation and VSWR
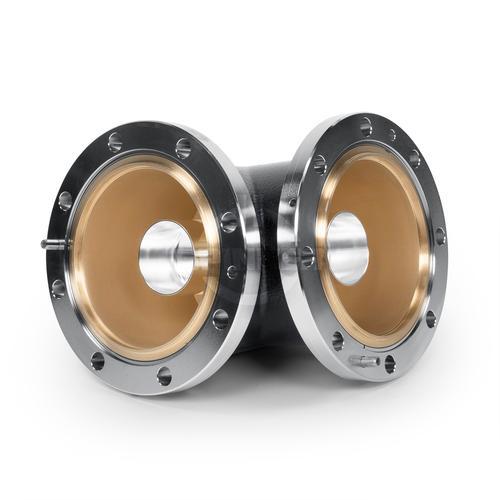
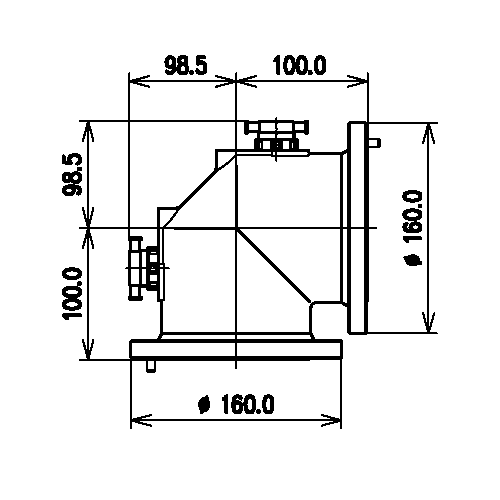
The Rigid line 90° elbow 4 1/2" EIA enables you to transmit high-frequency signals reliably and flawlessly with optimum protection of your sensitive equipment in a power range up to 112 kW @ 100 MHz (at +40 °C ambient temperature), 74 kW @ 230 MHz (at +40 °C ambient temperature), 38 kW @ 860 MHz (at +40 °C ambient temperature) with maximum passive intermodulation (IM3).
The positive characteristics are briefly summarised: very stable rigid line system, low insertion loss, low VSWR, PTFE insulation, designed for pressure-tight systems, for outdoor application.
Coaxial flange connectors, generally known as “EIA flanges”, are connected by a coupling element. The flange connector system complies with international standards EIA STD RS-225, 339 IEC, DIN EN 122150 and MIL-F 24044. The EIA flange connectors are excellently qualified suited for pressurized systems and for outdoor installations. 4 1/2" EIA connectors are used to link two elements of a rigid or semi-rigid high performance coaxial transmission line for radio frequency signals. Typically, these are operated in systems for very high power transmission (from kW to MW), e.g. in DAB, DVB or FM broadcast systems or in high-energy applications in research facilities (particle accelerator, plasmatron).
As rigid coaxial lines cannot be bent, you need a rigid coaxial line elbow section to route the waveguide into a new direction. There are two versions of elbows: SMS male and EIA female.